For some time now, I wanted to get HTTPS going using Letsencrypt on k3s distribution of Kubernetes using the Traefik Ingress.
For some time now, I wanted to get HTTPS going using Letsencrypt on k3s distribution of Kubernetes using the Traefik Ingress.I see a lot of guides online using the Nginx Ingress Controller, but due to K3s having Traefik enabled by default, and due to me being a die-hard fan of Traefik, I wanted to do a demonstration on how you can deploy your webapp to kubernetes and expose the service with a TLS encrypted endpoint using Letsencrypt Certificates for HTTPS using Traefik.
What are we doing
We will be installing v1.18.9 of k3s, install cert-manager for certificate management, then deploy a sample application which will be accessible using a https endpoint.
My DNS is configured for this demo as show below:
Record Type Value
k3s.ruan.dev A 95.179.189.16
*.k3s.ruan.dev CNAME k3s.ruan.devInstall k3s
Have a look at Rancher's Documentation for server configuration paramaneters, but in this case I will only be passing--tls-san, which adds an additional hostname or IP as a Subject Alternative Name in the TLS cert$ curl -sfL https://get.k3s.io | INSTALL_K3S_EXEC="--tls-san 95.179.189.16" sh -Once k3s has been started, we can use kubectl to test if our k3s instance is running:
$ kubectl get nodes --output wide
NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION INTERNAL-IP EXTERNAL-IP OS-IMAGE KERNEL-VERSION CONTAINER-RUNTIME
kubernetes Ready master 10m v1.18.9+k3s1 95.179.189.16 <none> Ubuntu 18.04.5 LTS 4.15.0-118-generic containerd://1.3.3-k3s2
As we can see, I am only running one node which will act as a k3s-agent as well.
Cert Manager
Cert Manager, is a native certificate management controller for Kubernetes, and if you want to go a bit deeper into cert-manager you can have a look at their documentationFirst, lets create the kubernetes namespace, called cert-manager:
$ kubectl create namespace cert-managerYou have a couple of options installing cert-manager such as helm, arkade, etc. But for this tutorial, I will be using their v0.11 manifests from github:
$ kubectl apply -f https://github.com/jetstack/cert-manager/releases/download/v0.11.0/cert-manager.yamlAfter a minute or so, verify that the cert-manager pods are running on their desired state:
$ kubectl get pods --namespace cert-manager
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
cert-manager-cainjector-75f88c9f56-zl2dw 1/1 Running 0 25s
cert-manager-77d8f4d85f-pnvxs 1/1 Running 0 25s
cert-manager-webhook-56669d7fcb-sj9n2 1/1 Running 1 25s
Once that is running we are going to use the kubernetes resource type ClusterIssuer to enable Letsencrypt to issue certificates for us.
We are naming this resource letsencrypt-prod and you will need to replace the email address withyour email address:
$ cat letsencrypt.yml
apiVersion: cert-manager.io/v1alpha2
kind: ClusterIssuer
metadata:
name: letsencrypt-prod
spec:
acme:
email: <your>@<email>.<com> # replace this
privateKeySecretRef:
name: prod-issuer-account-key
server: https://acme-v02.api.letsencrypt.org/directory
http01: {}
solvers:
- http01:
ingress:
class: traefik
selector: {}
Then deploy this to kubernetes:
$ kubectl apply -f letsencrypt.ymlWe can then describe our resource using the following:
$ kubectl describe clusterissuer letsencrypt
...
Status:
Acme:
Last Registered Email: [email protected]
Uri: https://acme-v02.api.letsencrypt.org/acme/acct/xxxxxxx
Conditions:
Last Transition Time: 2020-10-16T06:12:34Z
Message: The ACME account was registered with the ACME server
Reason: ACMEAccountRegistered
Status: True
Type: Ready
Events: <none>
Now we are ready to deploy our application.
Deploy the Web Application
We will deploy a basic application that serves a Rancher static image, the container runs on port 80 and we will be using the rancher tag, if you would like to check out the docker hub page for this image, head over to ruanbekker/logosFirst let's create our namespace on kubernetes where we want to deploy our application to, I will be using the namespace logos:
$ kubectl create namespace logosFirst we need to deploy our application, in our deployment.yml we are providing a name and the namespace our deployment must be deployed in, we are also providing selector labels rancher-logo-backend and you will notice our docker image ruanbekker/logos:rancer and that our container is listening on port 80:
$ cat deployment.yml
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: rancher-logo-app
namespace: logos
spec:
selector:
matchLabels:
name: rancher-logo-backend
template:
metadata:
labels:
name: rancher-logo-backend
spec:
containers:
- name: backend
image: ruanbekker/logos:rancher
ports:
- containerPort: 80
Deploy our application to kubernetes:
$ kubectl apply -f deployment.ymlVerify that the deployment is running in its desired state:
$ kubectl get deployment -n logos
NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE
rancher-logo-app 1/1 1 1 19s
We can also view our pod, by passing the key/value selector for our deployment:
$ kubectl get pods -n logos -l name=rancher-logo-backend
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
rancher-logo-app-7d845bb64-xmjlt 1/1 Running 0 119s
Next, we need to deploy a service resource to kubernetes, in our service.yml manifest, we are providing a name and the namespace where it should be deployed to, the port that we are defining for the service, which is important to take note of, as we will require this for our ingress.
Then we are defining the targetPort which is the port our container is listening on and the selector name=rancher-logo-backend:
$ cat service.yml
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: rancher-logo-service
namespace: logos
spec:
ports:
- name: http
port: 80
protocol: TCP
targetPort: 80
selector:
name: rancher-logo-backendDeploy the service to kubernetes:
$ kubectl apply -f service.ymlOnce our service has been deployed, we can verify using:
$ kubectl get service -n logos
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
rancher-logo-service ClusterIP 10.43.73.138 <none> 80/TCP 5m22s
Now we want to deploy our ingress, and this section we need to define the cluster issuer resource that we previously created, namely letsencrypt-prod in my case.
My FQDN for my web service will be rancher-logo.k3s.ruan.dev , my ingress class will be traefik and as mentioned above my cluster-issuer is letsencrypt-prod
Then lastly, you will see that we are routing the traffic to our service rancher-logo-service on port 80 of the service:
$ cat ingress.yml
apiVersion: extensions/v1beta1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
name: rancher-logo-ingress
namespace: logos
annotations:
kubernetes.io/ingress.class: traefik
cert-manager.io/cluster-issuer: letsencrypt-prod
spec:
tls:
- secretName: rancher-logo-k3s-ruan-dev-tls
hosts:
- rancher-logo.k3s.ruan.dev
rules:
- host: rancher-logo.k3s.ruan.dev
http:
paths:
- path: /
backend:
serviceName: rancher-logo-service
servicePort: 80
Deploy the ingress to kubernetes:
$ kubectl apply -f ingress.ymlOnce your ingress has been deployed, you will notice that another ingress comes up, when you view your ingresses:
$ kubectl get ingress -n logos
NAME CLASS HOSTS ADDRESS PORTS AGE
rancher-logo-ingress <none> rancher-logo.k3s.ruan.dev 80, 443 4s
cm-acme-http-solver-ncvdv <none> rancher-logo.k3s.ruan.dev 95.179.189.16 80 1s
This is due to the http challenge we provided in our cluster issuer. To get the status of the certificate request, we can describe the certificate resource:
$ kubectl -n logos describe certificate
...
Status:
Conditions:
Last Transition Time: 2020-10-16T06:53:14Z
Message: Waiting for CertificateRequest "rancher-logo-k3s-ruan-dev-tls-2207795628" to complete
Reason: InProgress
Status: False
Type: Ready
Events:
Type Reason Age From Message
---- ------ ---- ---- -------
Normal Requested 11s cert-manager Created new CertificateRequest resource "rancher-logo-k3s-ruan-dev-tls-2207795628"
After a minute or so when we look again, we can see that the certificate has been issued:
$ kubectl describe certificate -n logos
...
Events:
Type Reason Age From Message
---- ------ ---- ---- -------
Normal Requested 27s cert-manager Created new CertificateRequest resource "rancher-logo-k3s-ruan-dev-tls-2207795628"
Normal Issued 1s cert-manager Certificate issued successfully
When we look at our ingress again, we will only see our ingress that we deployed:
$ kubectl get ingress -n logos
NAME CLASS HOSTS ADDRESS PORTS AGE
rancher-logo-ingress <none> rancher-logo.k3s.ruan.dev 95.179.189.16 80, 443 31s
Test our Web Application
Let's test our web application using a browser, in my case rancher-logo.k3s.ruan.dev:

And we can see that our certificate is valid, issued by Letsencrypt:
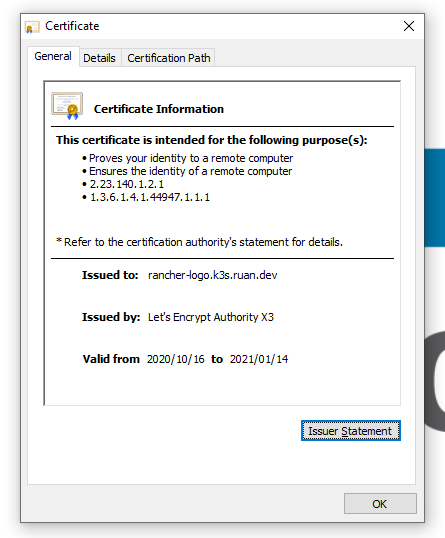
HTTPS ftw!
Thank You
Thanks for reading, if you enjoy my content feel free to follow me on Twitter at @ruanbekker, visit my website and subscribe to my newsletter.

Comments